CURRENT ISSUE
EDITOR'S PICKS
Review Series on myeloproliferative neoplasms
Prevention, diagnosis and management of myeloproliferative neoplasms: an introduction to a review series
Prevention and treatment of transformation of myeloproliferative neoplasms to acute myeloid leukemia
Evolution of myeloproliferative neoplasms from normal blood stem cells
New approaches to standard of care in early-phase myeloproliferative neoplasms: can interferon-α alter the natural history of the disease?
Pathogenesis and management of high molecular risk myeloproliferative neoplasms
ARTICLES IN THREE SENTENCES
Letter
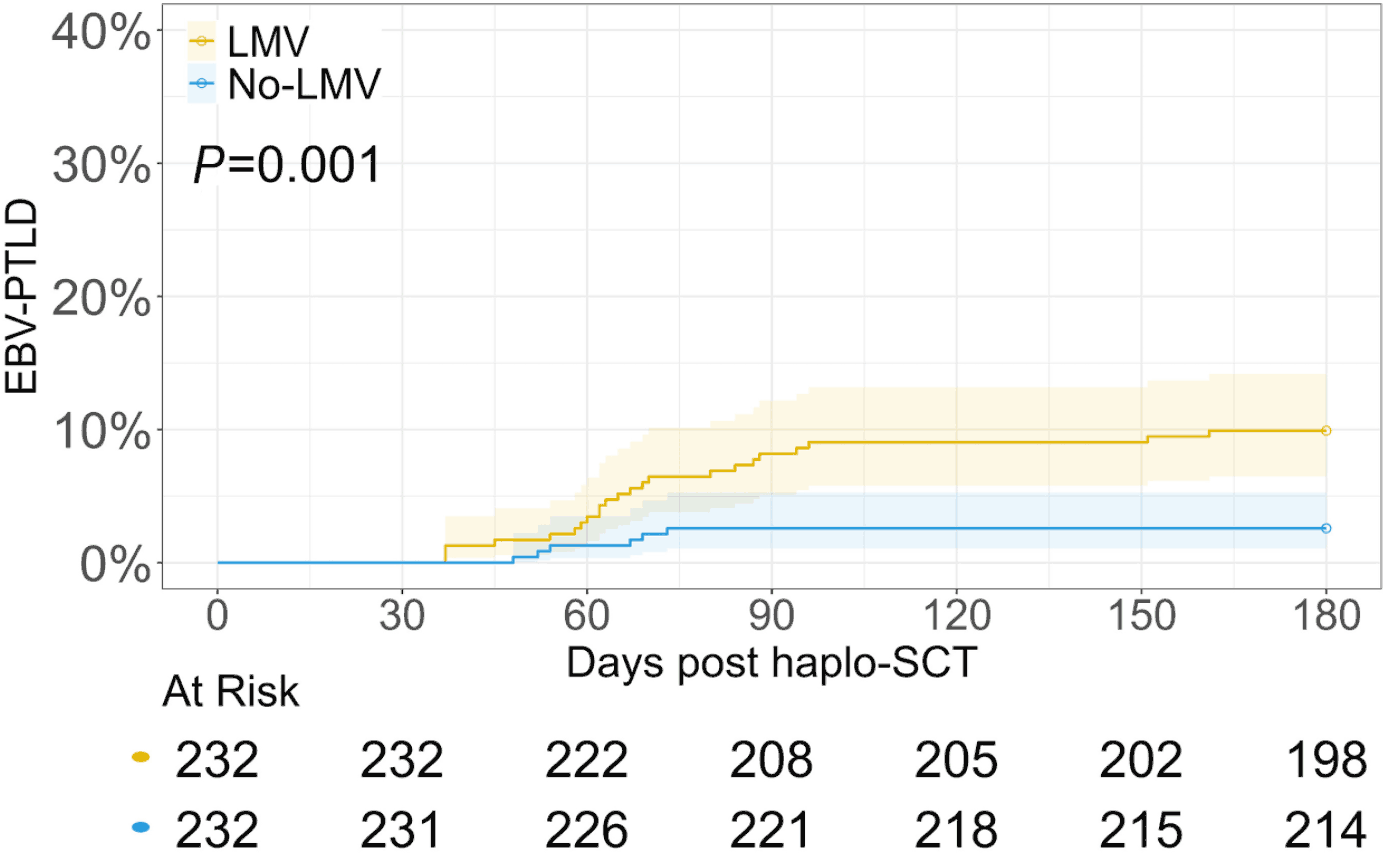
Letermovir prophylaxis for cytomegalovirus is associated with risk of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders after haploidentical stem cell transplantation
Letermovir prophylaxis effectively reduces cytomegalovirus infection after haploidentical stem cell transplantation; however, its impact on Epstein-Barr virus remains unclear. The study by Pei and colleagues compared letermovir recipients to a control group receiving standard polymerase chain reaction-guided pre-emptive therapy in two independent cohorts. While the incidence of EBV viremia was similar in the two groups, letermovir recipients exhibited higher peak EBV titers and had an increased risk of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorder within the first 180 days, highlighting the need for caution and further research to explore this potential link in clinical practice.
Letter
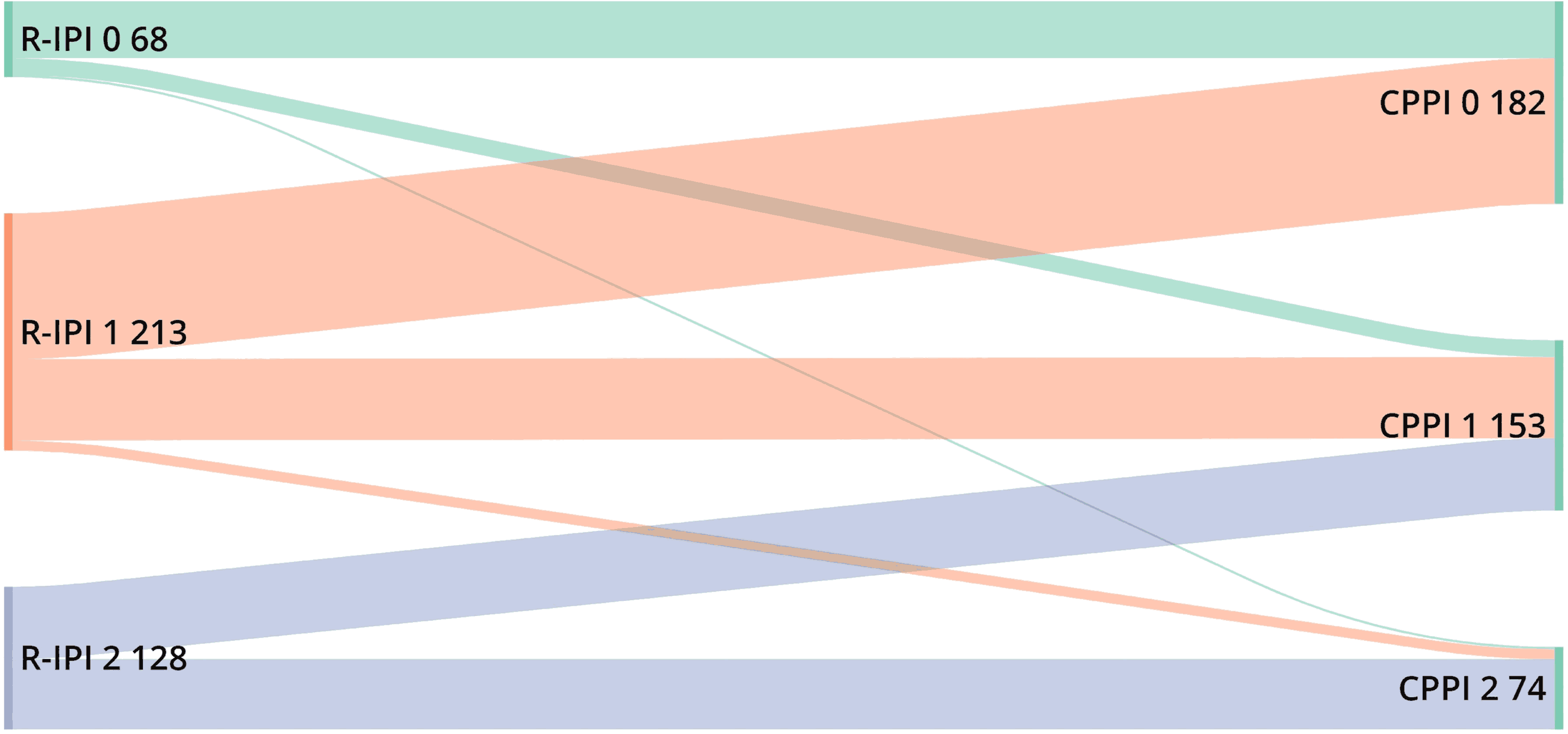
Identification of a clinicopathologic prognostic index for newly diagnosed large B-cell lymphoma patients treated with R-CHOP
Tumor features have not been routinely incorporated into a prognostic risk score for patients with newly diagnosed large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) treated with R-CHOP. In a cohort of >400 newly diagnosed LBCL patients, Ni and colleagues identified three risk factors – International Prognostic Index (IPI) score of ≥3, double expressor lymphoma, and TP53 loss of function mutation – which are independently predictive of inferior 2-year progression-free and overall survival. Starting from that, they developed a novel Clinicopathologic Prognostic Index (CPPI), which outperformed the revised-IPI in identifying a limited cohort of patients who experienced inferior survival outcomes.
Letter
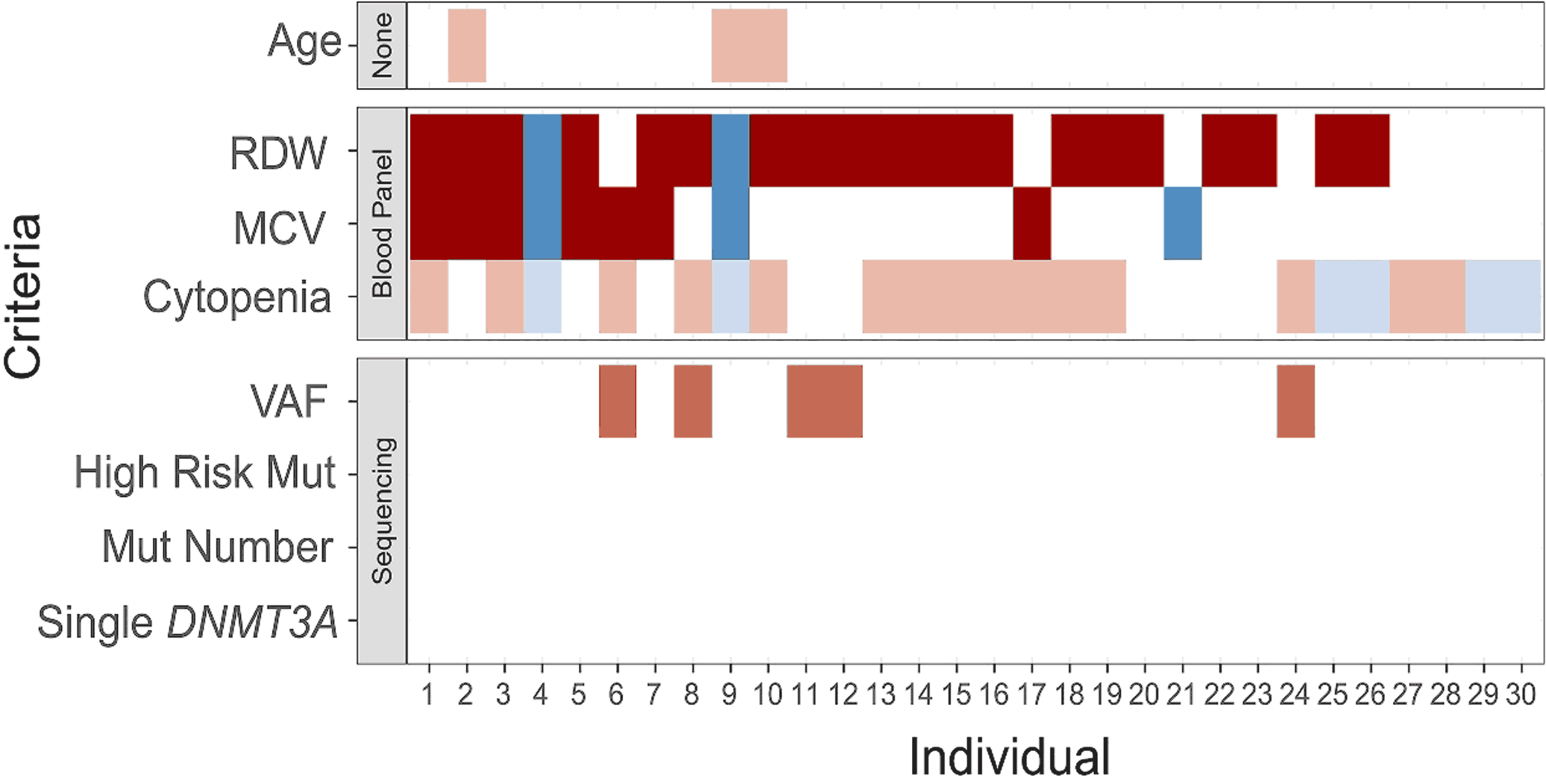
Germline genetics, disease, and exposure to medication influence longitudinal dynamics of clonal hematopoiesis
Variant allele fraction (VAF) defining clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) exceeds 2%, and higher VAF is associated with increased morbidity and mortality risk. To identify factors influencing clonal expansion and consequently risk stratification of CHIP patients, Mack and colleagues performed targeted, error-corrected sequencing on serial blood samples from 3,000 individuals. Their study reveals that CHIP growth rates vary significantly by driver gene and are influenced by germline variants and medication exposures, and that monitoring blood counts may be more informative for risk stratification than frequent resequencing in CHIP patients.
Letter
Isatuximab, pomalidomide, and dexamethasone as salvage therapy for patients with multiple myeloma: the Italian, multicenter, retrospective clinical experience with 270 cases outside of controlled clinical trials
The pivotal ICARIA-MM trial, demonstrated a significant improvement in progression-free survival for patients treated with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) treated with isatuximab-pomalidomide-dexamethasone (IsaPd), compared to pomalidomide-dexamethasone alone. Martino and colleagues conducted a real-world study analyzing 270 RRMM patients treated with IsaPd. Results show that IsaPd is effective and safe in a real-world setting for RRMM patients, but alternative therapeutic strategies are needed for the high-risk and daratumumab-exposed patients.
TAKE ADVANTAGE FROM HAEMATOLOGICA





