CURRENT ISSUE
EDITOR'S PICKS
Review Series on venous thromboembolism
Introduction to the Review Series on venous thromboembolism: emerging issues in pathophysiology and management
Multimorbidity, comorbidity, frailty, and venous thromboembolism
Minor trauma and venous thromboembolism: the threshold for antithrombotic prophylaxis
Targeted anti-cancer agents and risk of venous thromboembolism
ARTICLES IN THREE SENTENCES
Article
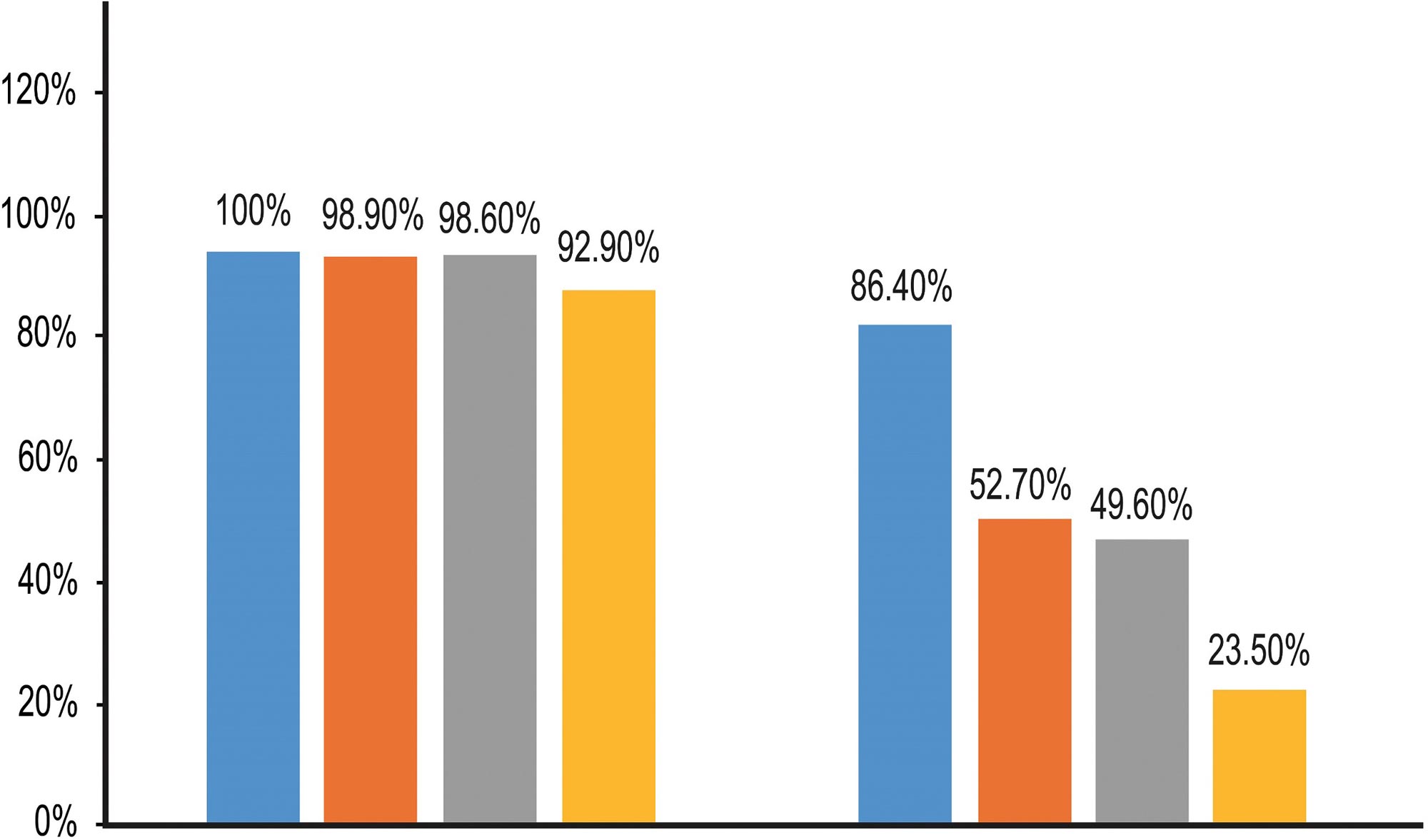
Safety and efficacy of flumatinib as later-line therapy in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia
Flumatinib mesylate, a second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), is a derivative of imatinib and in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has greater selectivity and potency compared with imatinib, and a lower rate of side effects. However, there are no real-world data. Yang and colleagues show results of a multicenter, retrospective, observational study analyzing the efficacy and safety of flumatinib in the later-line setting in CML patients who were resistant or intolerant to previous TKI therapy. They demonstrated that flumatinib is effective and safe in this cohort, and in particular, second-line use induced high response rates.
Article
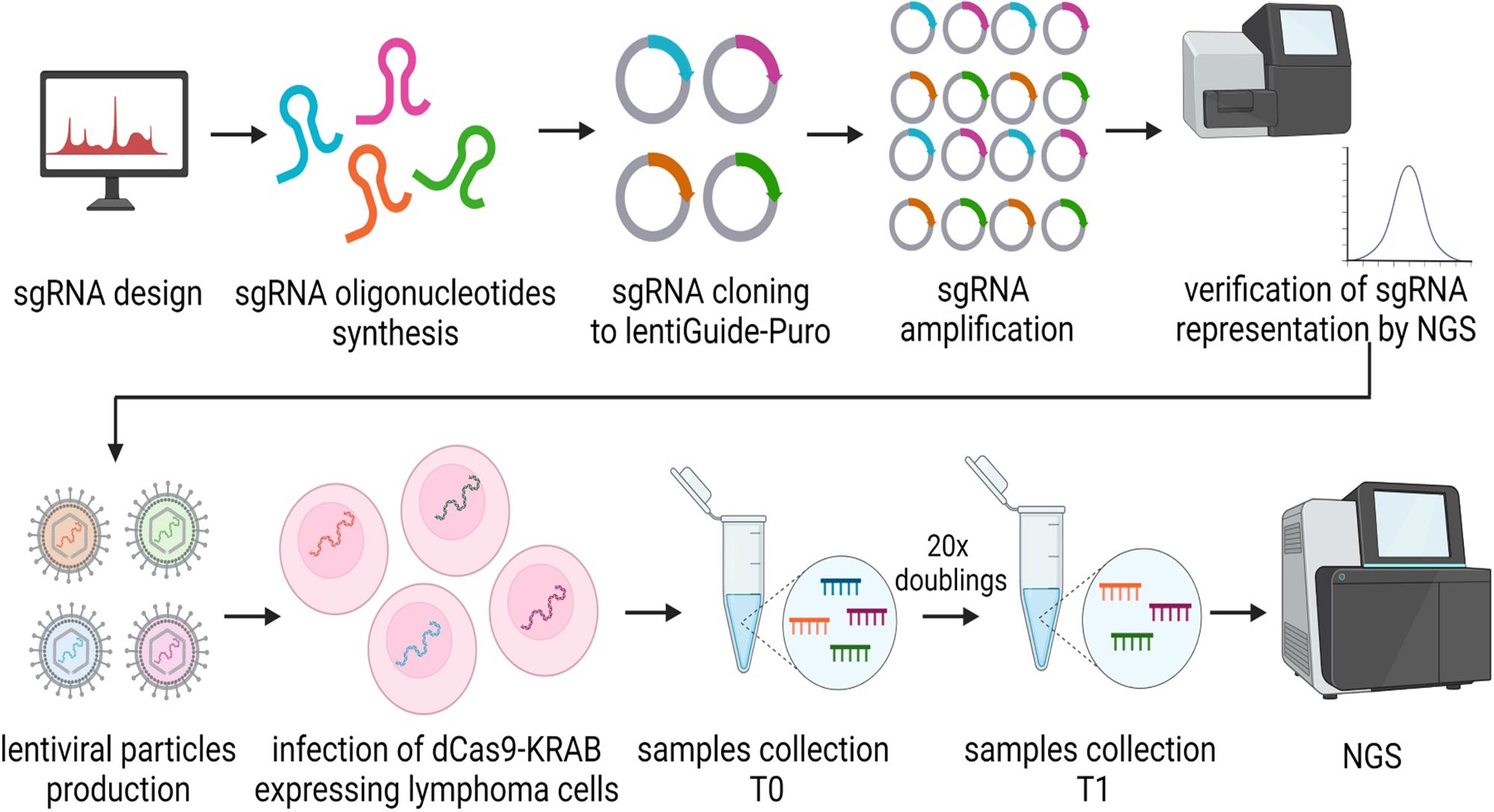
Core regions in immunoglobulin heavy chain enhancers essential for survival of non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells are identified by a CRISPR interference screen
The precise role of immunoglobulin heavy chain (IGH) enhancers in the control of translocated oncogenes in non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) is not completely understood. In order to define the critical regions in the IGH regulatory elements and identify enhancer RNA, Kasprzyk and colleagues designed a single-guide RNA library densely covering the IGH enhancers and performed tiling CRISPR interference screens in three NHL cell lines. Their results indicated the most critical regions in the IGH enhancers and provided new insights into the current understanding of the role of IGH enhancers in B-cell NHL.
Article
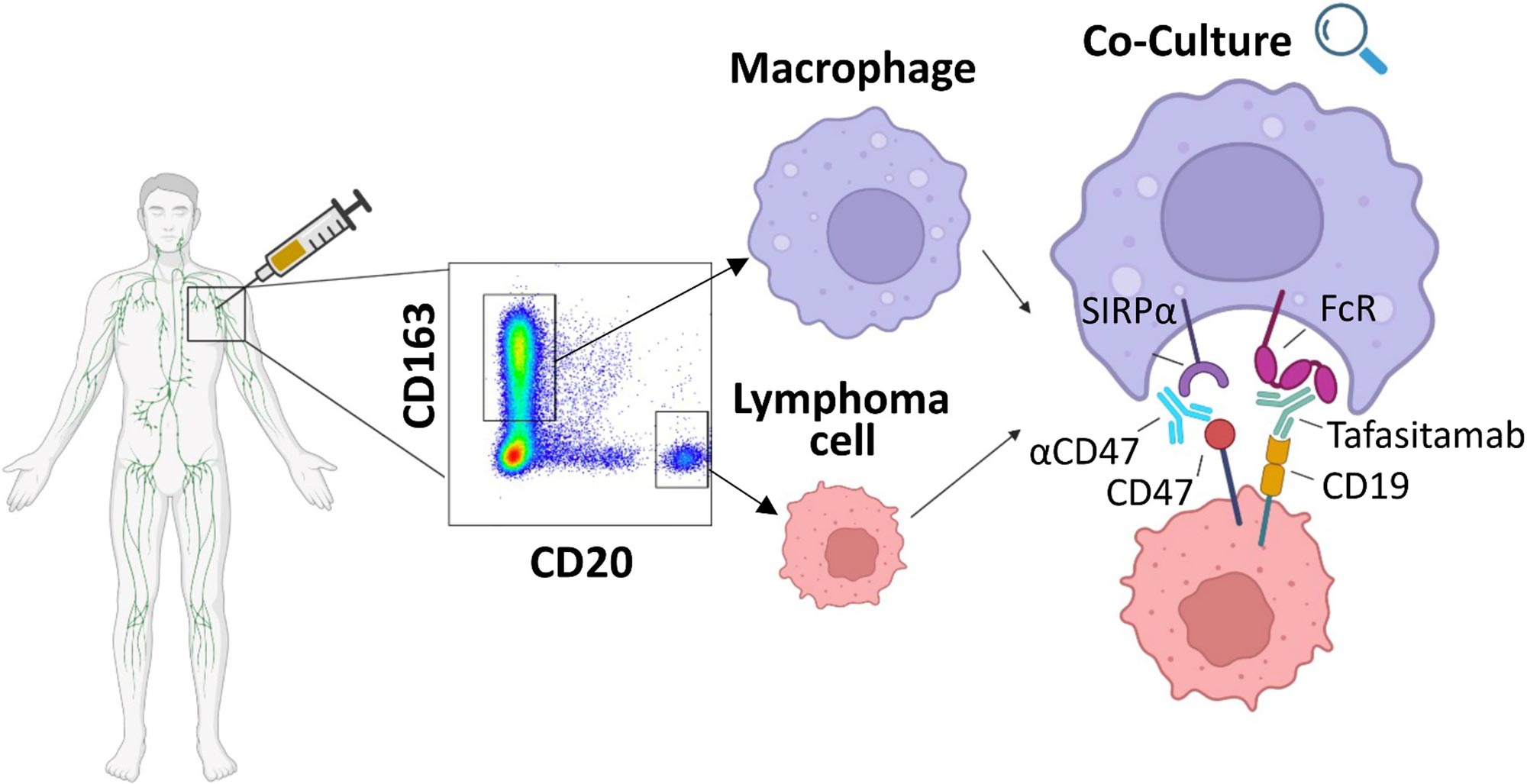
Blockade of the CD47/SIRPα checkpoint axis potentiates the macrophage-mediated antitumor efficacy of tafasitamab
The anti-CD19 antibody tafasitamab is approved in combination with lenalidomide for the treatment of relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Biedermann and colleagues investigate the impact of the CD47-SIRPα axis on tafasitamab-mediated phagocytosis and explore the potential of anti-CD47 blockade to enhance its antitumor activity. They demonstrated in lymphoma xenograft mouse models that a combination of tafasitamab and an anti-CD47 antibody resulted in greater tumor volume reduction and survival benefit, providing evidence that CD47 blockade can enhance the phagocytic potential of tumor-targeting immunotherapies and suggesting the opportunity to explore the combination in the clinical setting.
Letter
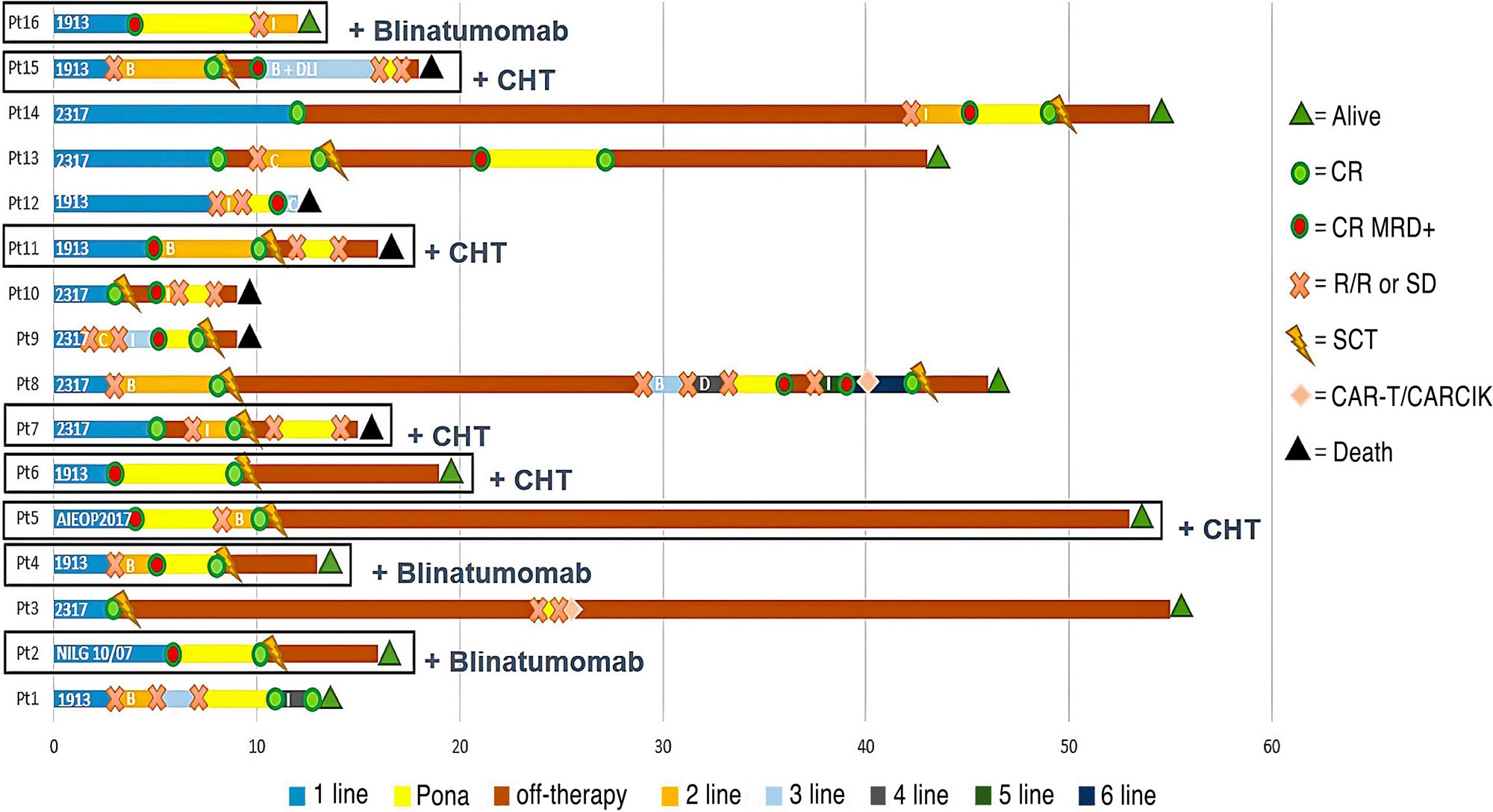
Ponatinib alone or with chemo-immunotherapy in heavily pre treated Philadelphia-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a CAMPUS ALL real-life study
Specific targeted therapies for Philadelphia-like acute lymphoblastic leukemia (Ph-like ALL) are still not available, however, preliminary in vitro data suggest that ponatinib could be effective for the management of Ph-like ALL regardless of underlying molecular abnormalities and there are case reports on its clinical use. The Italian Campus ALL network collected data on the ad hoc individual use of ponatinib for Ph-like ALL patients. The findings, reported by Kaiser and colleagues, confirm and extend, in a larger series of patients, the observation that ponatinib may be a cost-effective, easily accessible compound with an acceptable toxicity profile for Ph-like ALL patients, especially those with minimal residual disease.
TAKE ADVANTAGE FROM HAEMATOLOGICA





