CURRENT ISSUE
February, 2026
No. 111 (2)
2024 Impact Factor: 7.9
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
EDITOR'S PICKS
ARTICLES IN THREE SENTENCES
Article
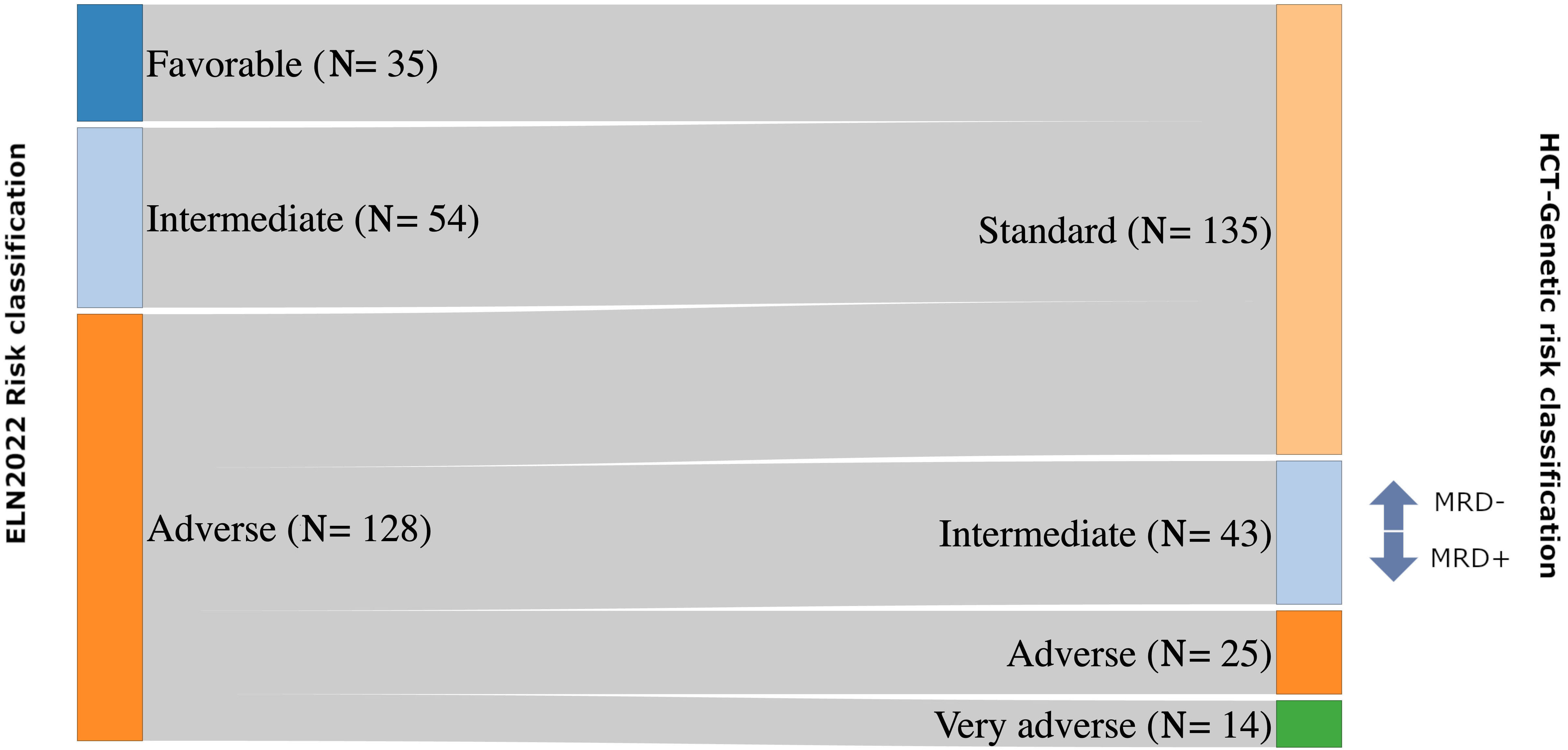
Genetic risk classification in acute myeloid leukemia patients treated with hematopoietic cell transplantation and post-transplant cyclophosphamide
The exact predictive value of the European LeukemiaNet (ELN) 2022 classification in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients undergoing allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT) is still under debate. A new study evaluates the prognostic value of genetic classification and measurable residual disease in AML patients undergoing allogeneic HCT with myeloablative conditioning regimens and post-transplant cyclophosphamide-based graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis. Four risk categories with distinct impact on survival and relapse risk have been identified, improving the prognostic value of ELN 2022.
Letter
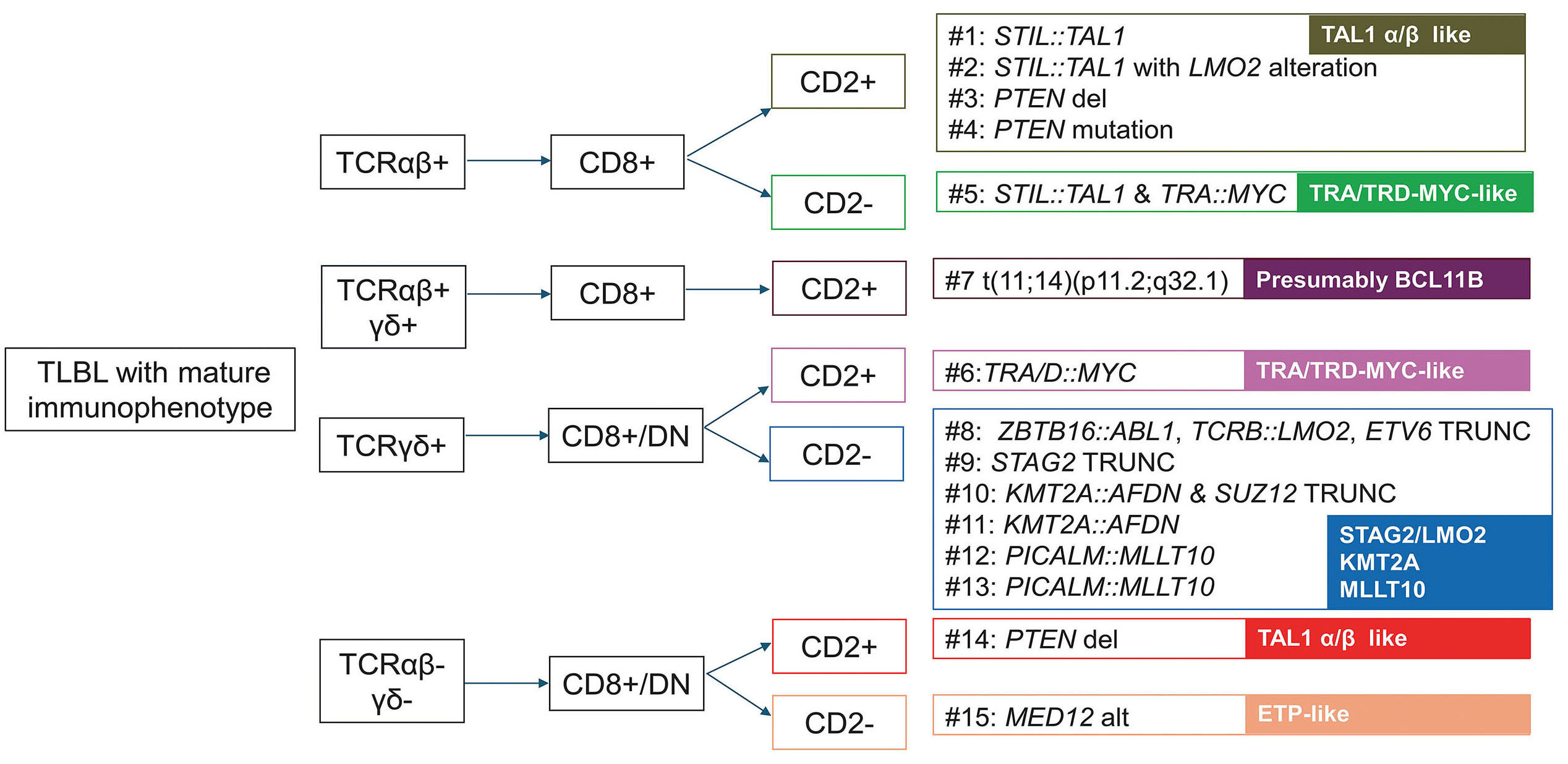
The immunophenotypic and genetic characterization of pediatric T-lymphoblastic leukemia with a mature immunophenotype
T-lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) in children is typically diagnosed by identifying immature T-cell markers, but rare cases present with a mature immunophenotype that can mimic other T-cell neoplasms. In this study, the authors performed detailed immunophenotypic and genetic profiling of pediatric T-ALL cases exhibiting a mature marker profile to define their distinguishing features. Results show that these leukemias have underlying genetic and immunophenotypic hallmarks of T-ALL, underscoring the importance of integrated diagnostic assessment to avoid misclassification and ensure appropriate therapy.
Article
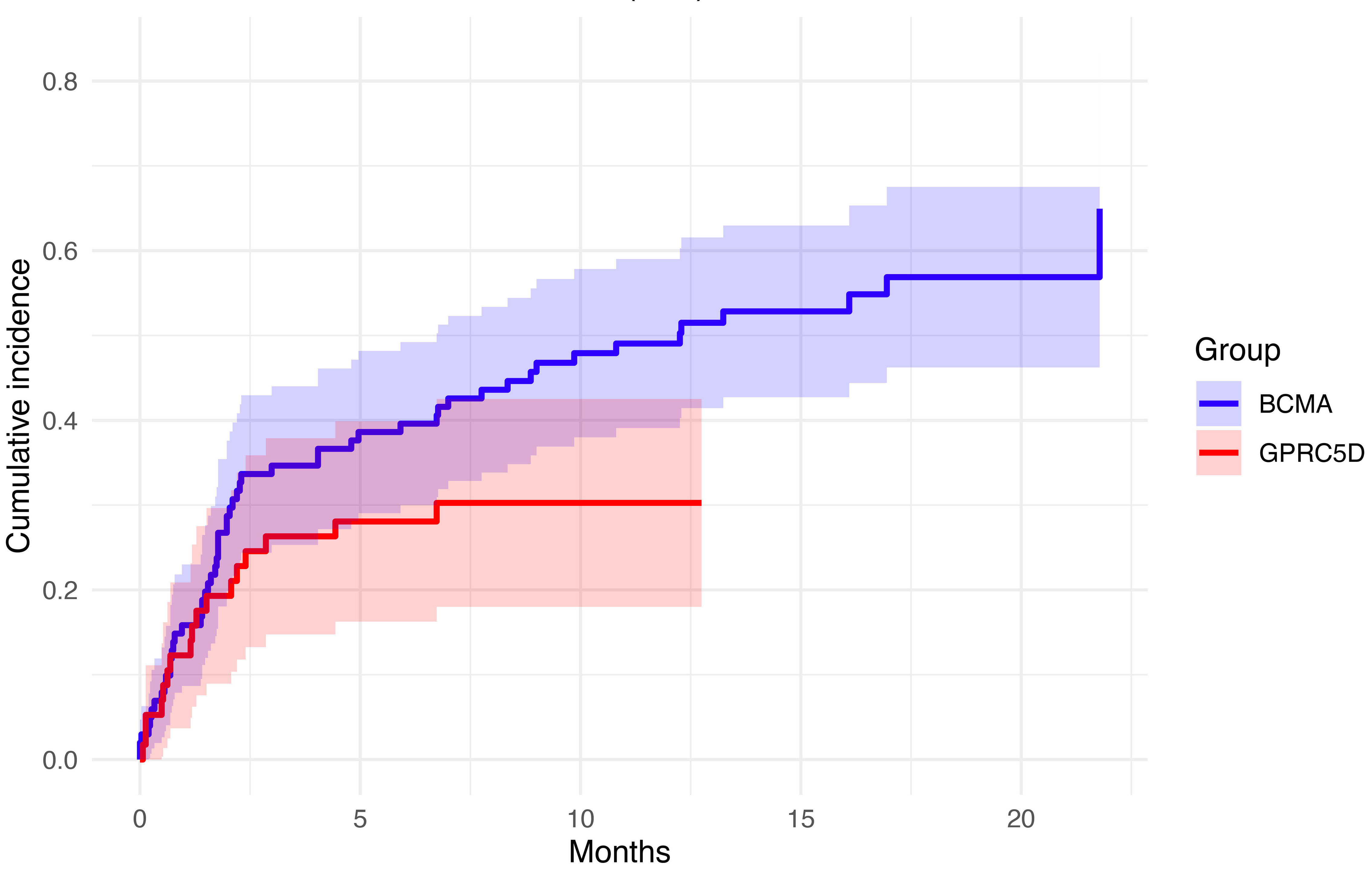
Infection risk in 158 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma treated with bispecific antibodies: a single-center experience
Four bispecific antibodies (BsAb) are approved for the treatment of relapsed refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM), but their use is associated with infection risks, requiring mitigation strategies. Cani and colleagues analyzed a cohort of RRMM patients treated with BsAb in clinical practice, with the aim of characterizing the incidence, timing, and risk factors associated with infections. Results showed a higher incidence of any-grade infections, especially cytomegalovirus reactivations, in patients receiving anti-BCMA BsAb and a role of primary intravenous immunoglobulin prophylaxis in reducing severe infections.
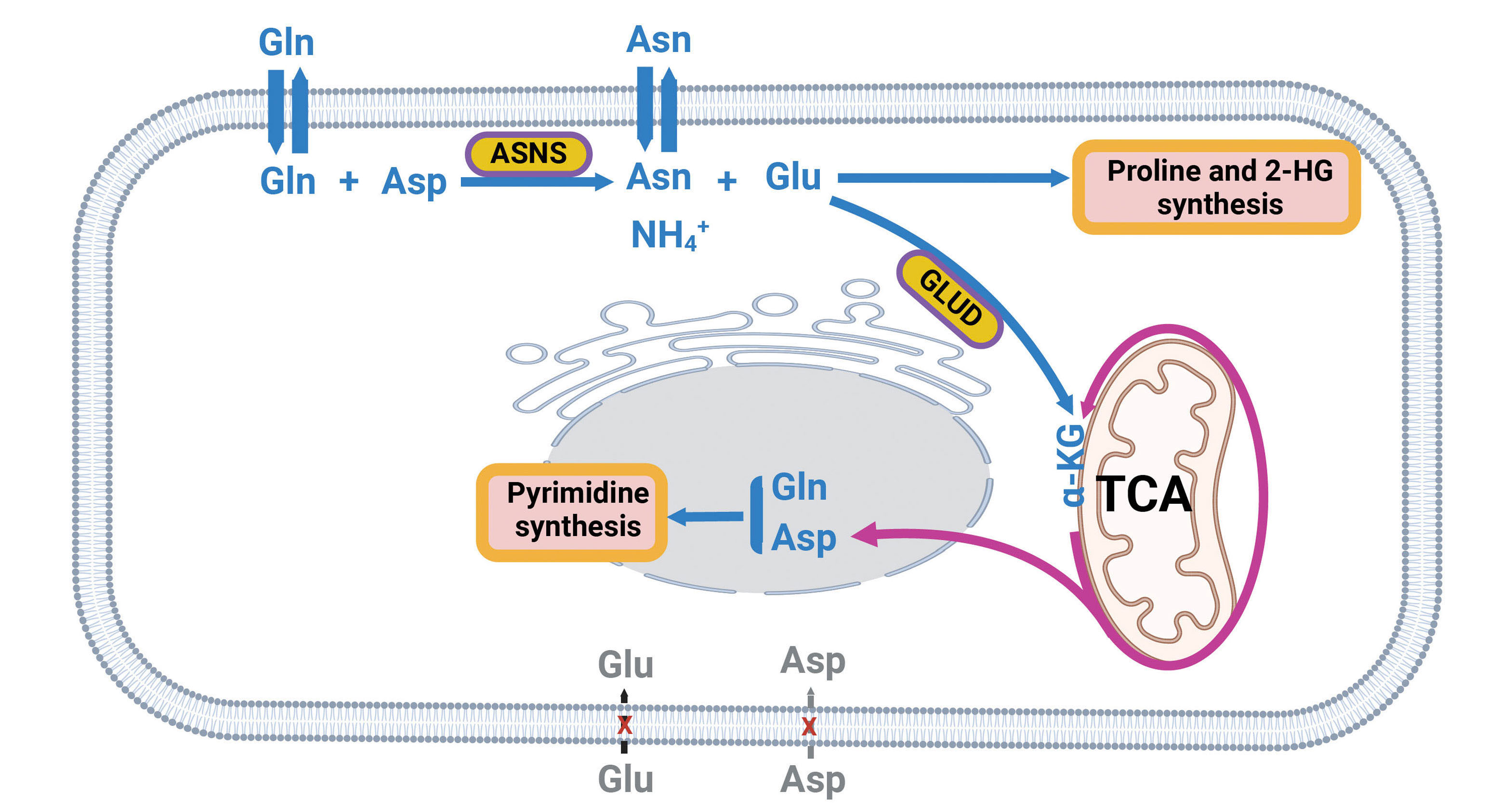
Letter
The glutaminase activity of ASNS fuels glutamine metabolism in leukemia
Glutamine metabolism is critical for leukemia cell growth and survival, yet the enzymatic pathways remain incompletely defined. The study by Chan et al. demonstrates that asparagine synthetase (ASNS) has effects on glutamine deamidation and metabolism with a functional glutaminase activity. This unexpected metabolic role for ASNS highlights it as a potential therapeutic vulnerability in leukemia.Targeting ASNS alone or in combination with other metabolic inhibitors offers a promising approach for the treatment of hematologic and non-hematologic cancers.
TAKE ADVANTAGE FROM HAEMATOLOGICA