ISSUE
January, 2024
No. 109 (1)
2024 Impact Factor: 7.9
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
2024 Journal Citation Indicator: 1.9
2024 CiteScore: 11.3
EDITOR'S PICKS
ARTICLES IN THREE SENTENCES
Article
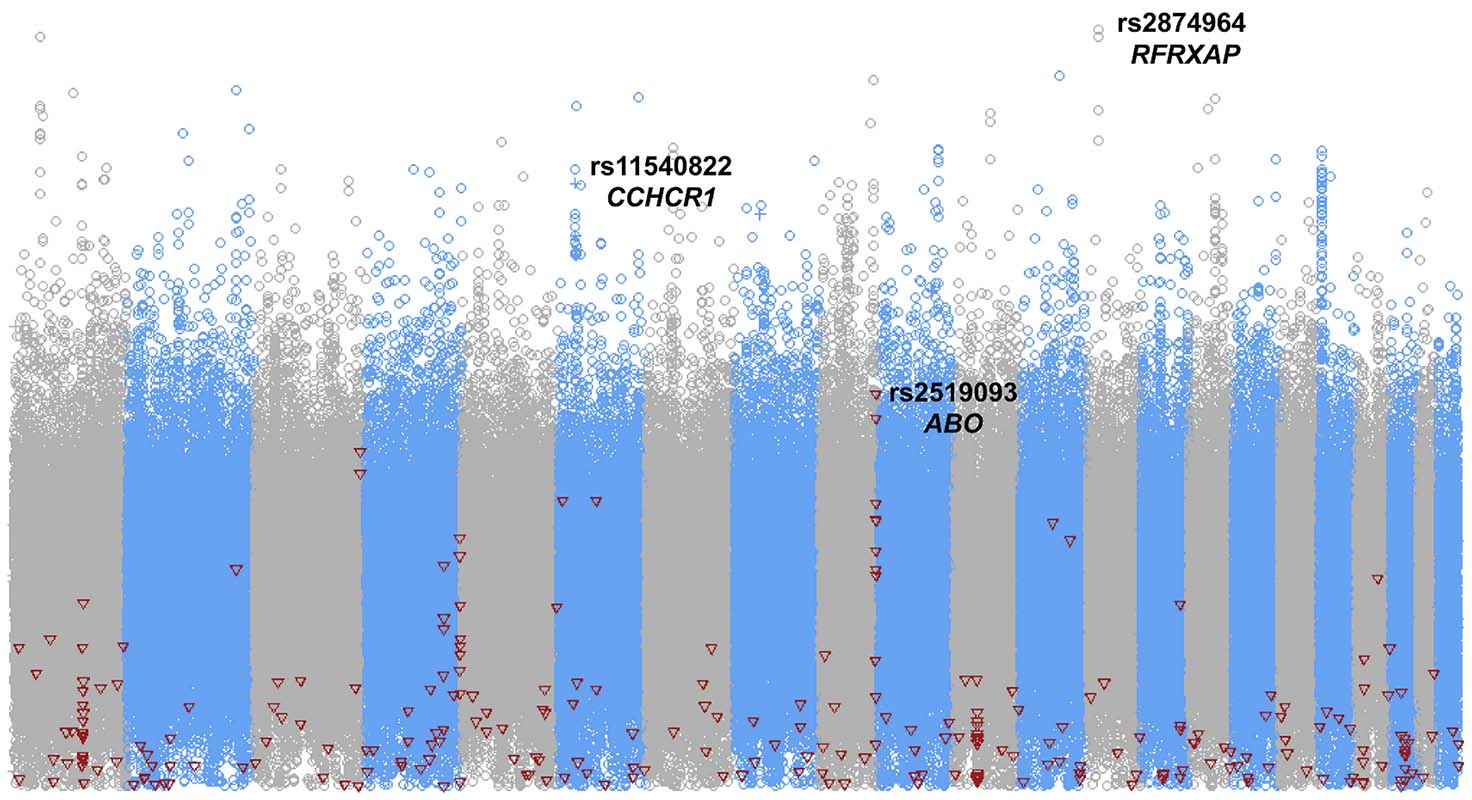
Genomic analysis of venous thrombosis in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia from diverse ancestries
Some studies have demonstrated a higher risk of venous thrombosis among Americans of African ancestry than among those of European ancestry in both the general population and adults with cancer. Zheng and colleagues performed a retrospective cohort evaluation of thrombosis risk in 1,005 ancestrally diverse children treated for newly diagnosed acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). In this cohort, clinical rather than genetic factors dominated the risk of thrombosis and genetic risks aggregated in erythrocyte-related single nucleotide polymorphisms, suggesting the critical role of red cells in this phenomenon. This study provides opportunities to target prophylactic interventions to reduce thrombosis in children treated for ALL.
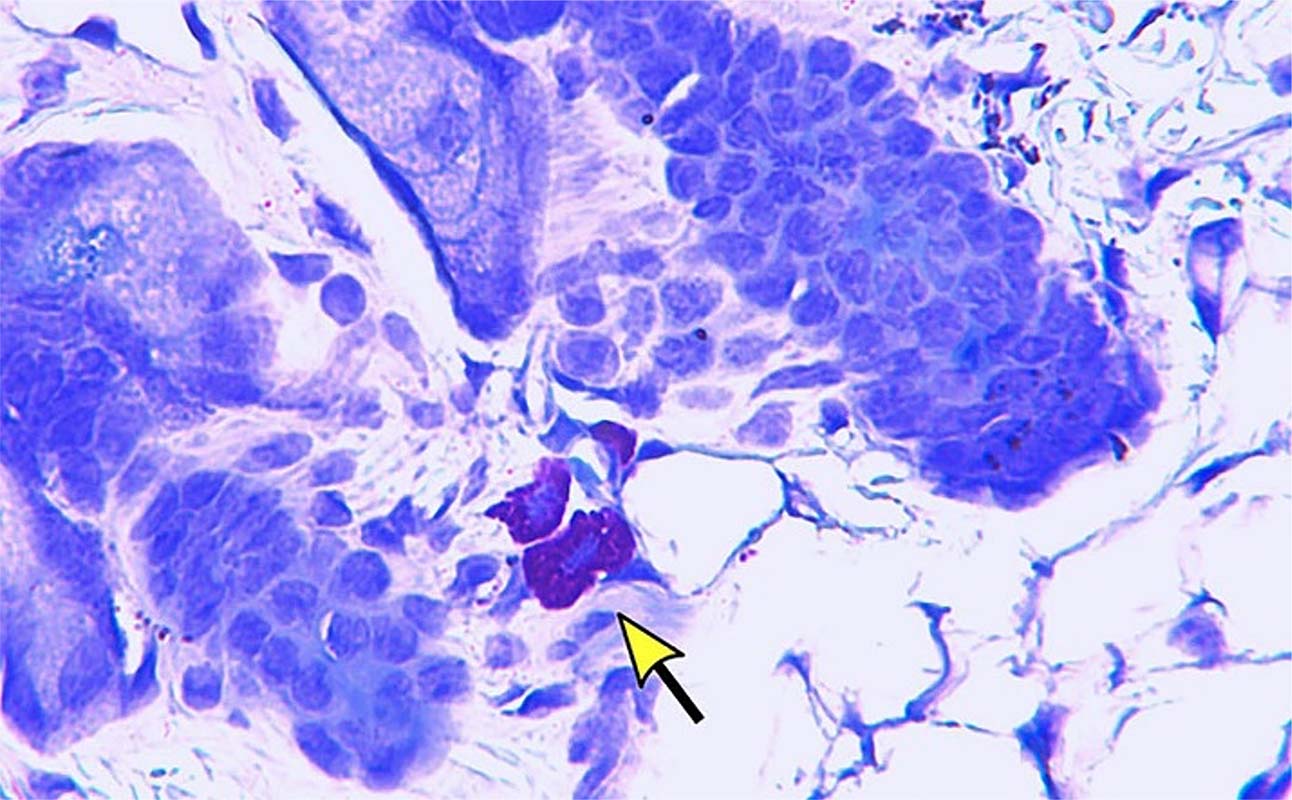
Letter
Colchicine reduces inflammation in a humanized transgenic murine model of sickle cell disease
Since sickle cell diseases (SCD) pathobiology includes activation of the innate immune system with sterile inflammation and a “cytokine storm”, introduction of a drug that targets SCD inflammation might improve outcomes. Fouda and colleagues hypothesized that colchicine, a drug used for the treatment or prevention of symptoms of gout and other non-infectious inflammatory conditions, might reduce inflammation and improve the clinical course of SCD. They demonstrated reduced inflammation after colchicine treatment in the HbSS-BERK humanized transgenic mouse model of SCD and speculated that colchicine could benefit patients with this disorder.
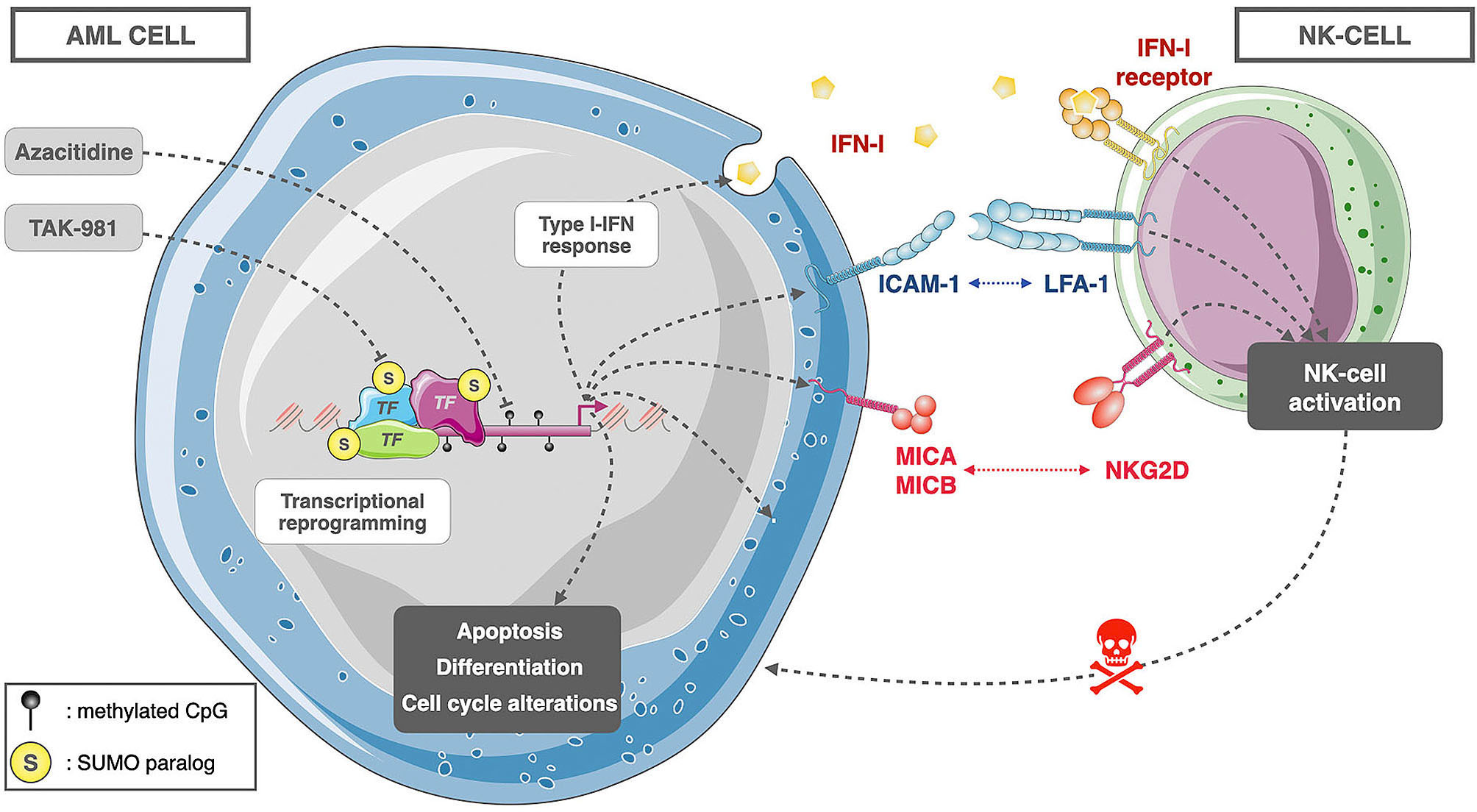
Article
SUMOylation inhibitor TAK-981 (subasumstat) synergizes with 5-azacytidine in preclinical models of acute myeloid leukemia
SUMOylation, a post-translational modification, plays key roles in leukemogenesis and response of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) to therapies, making the inhibition of SUMOylation a new potential therapeutic strategy in AML. TAK-981 is a first-in-class SUMO E1 inhibitor with very high potency and specificity. Gabellier and colleagues studied the efficacy of TAK-981 in various preclinical models of AML, AML cell lines and patients’ blast cells in vitro and in vivo in xenografted mice, and showed high and promising anti-leukemic activity of TAK-981 in combination with azacytidine.
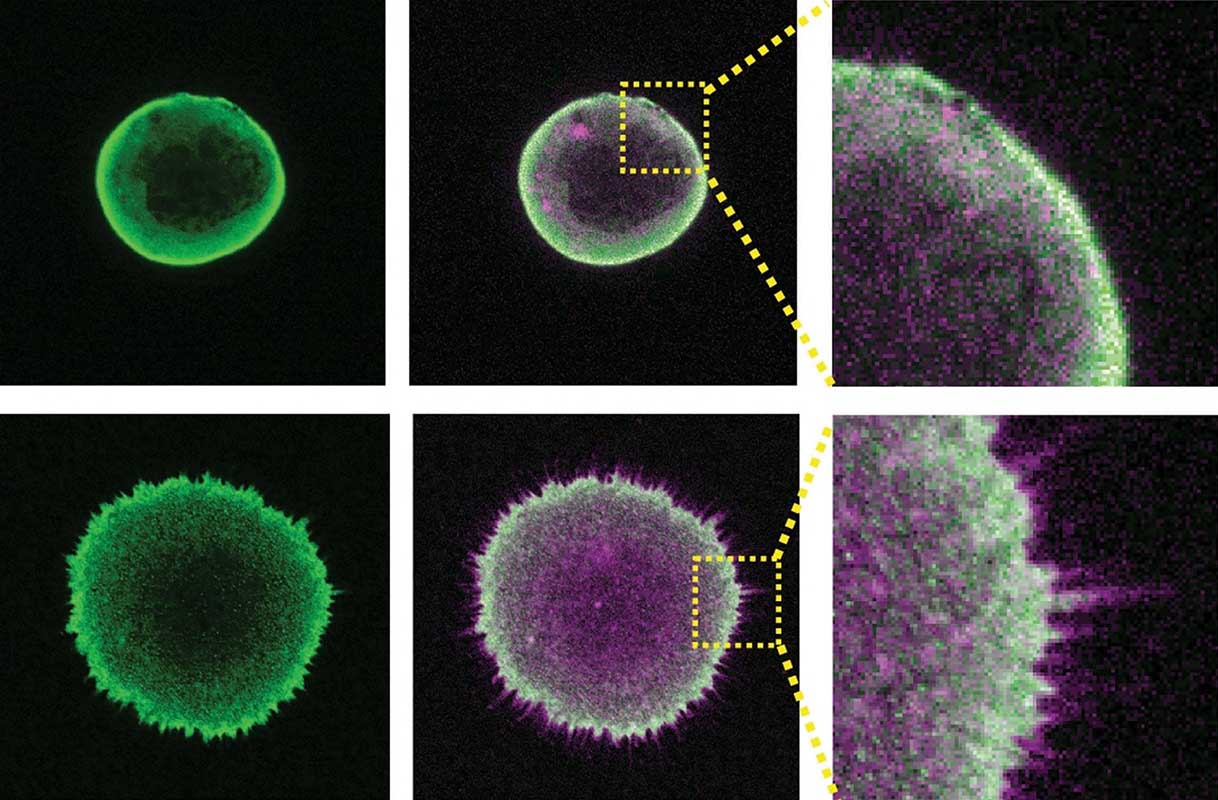
Letter
Actin-bundling protein L-plastin promotes megakaryocyte rigidity and dampens proplatelet formation
Despite the advancement of knowledge on the various stages of megakaryocyte (MK) differentiation, the molecular mechanisms promoting proplatelets formation (PPF) are not well understood. Recently, Guo’s laboratory identified an actin bundling protein, L-plastin, that decreases during MK differentiation and correlates with the onset of PPF. In the present study they measured MK cytoskeleton stiffness for the first time and found that it plays an important role in PPF, in that mice deficient in L-plastin showed increased MK PPF/higher platelet counts, and mouse and human MK L-plastin levels correlated strongly with MK membrane rigidity.
TAKE ADVANTAGE FROM HAEMATOLOGICA





